Aloe Vera
Botanical Name: Aloe vera
Common Name(s): Aloe Vera, Medicinal Aloe, Barbadenensis
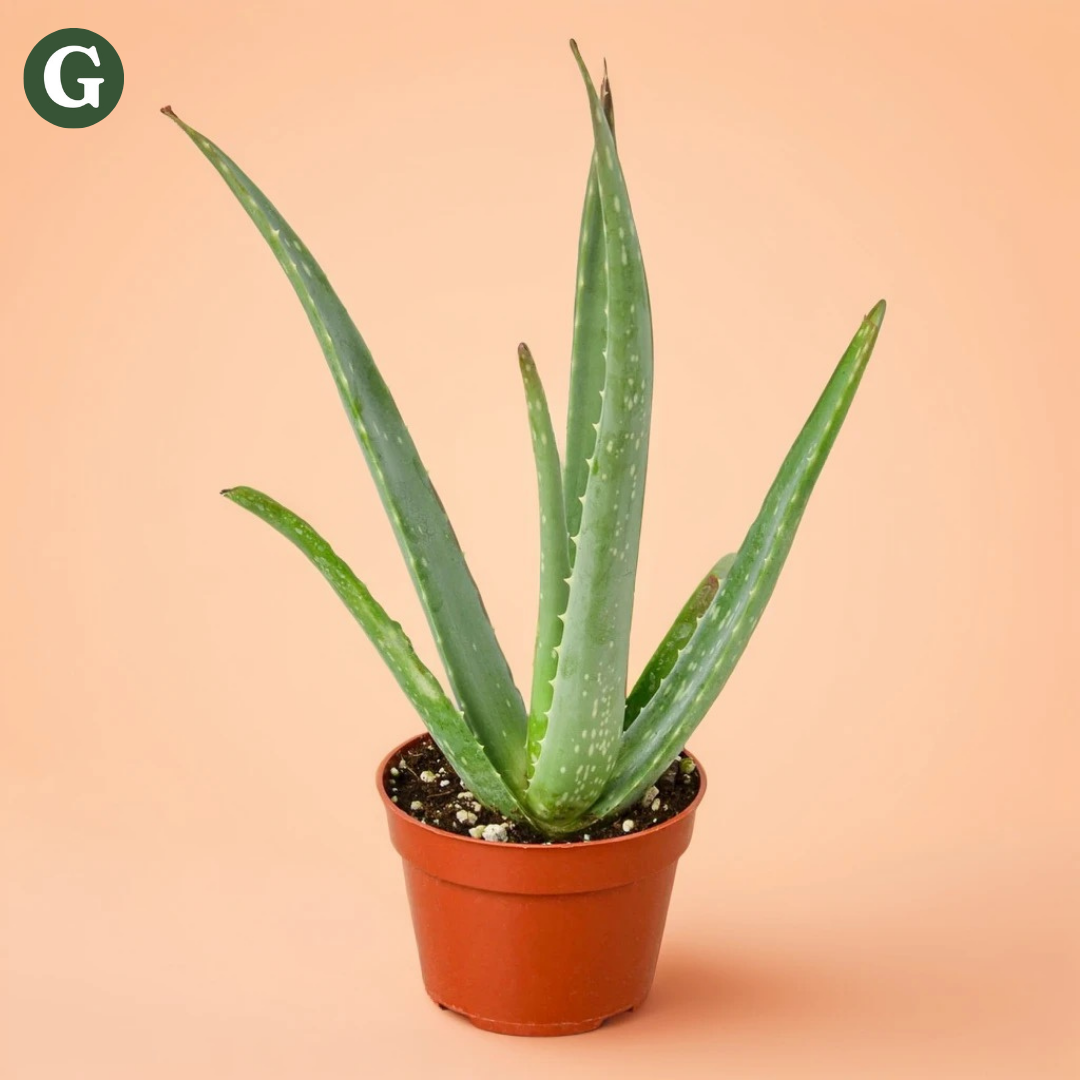
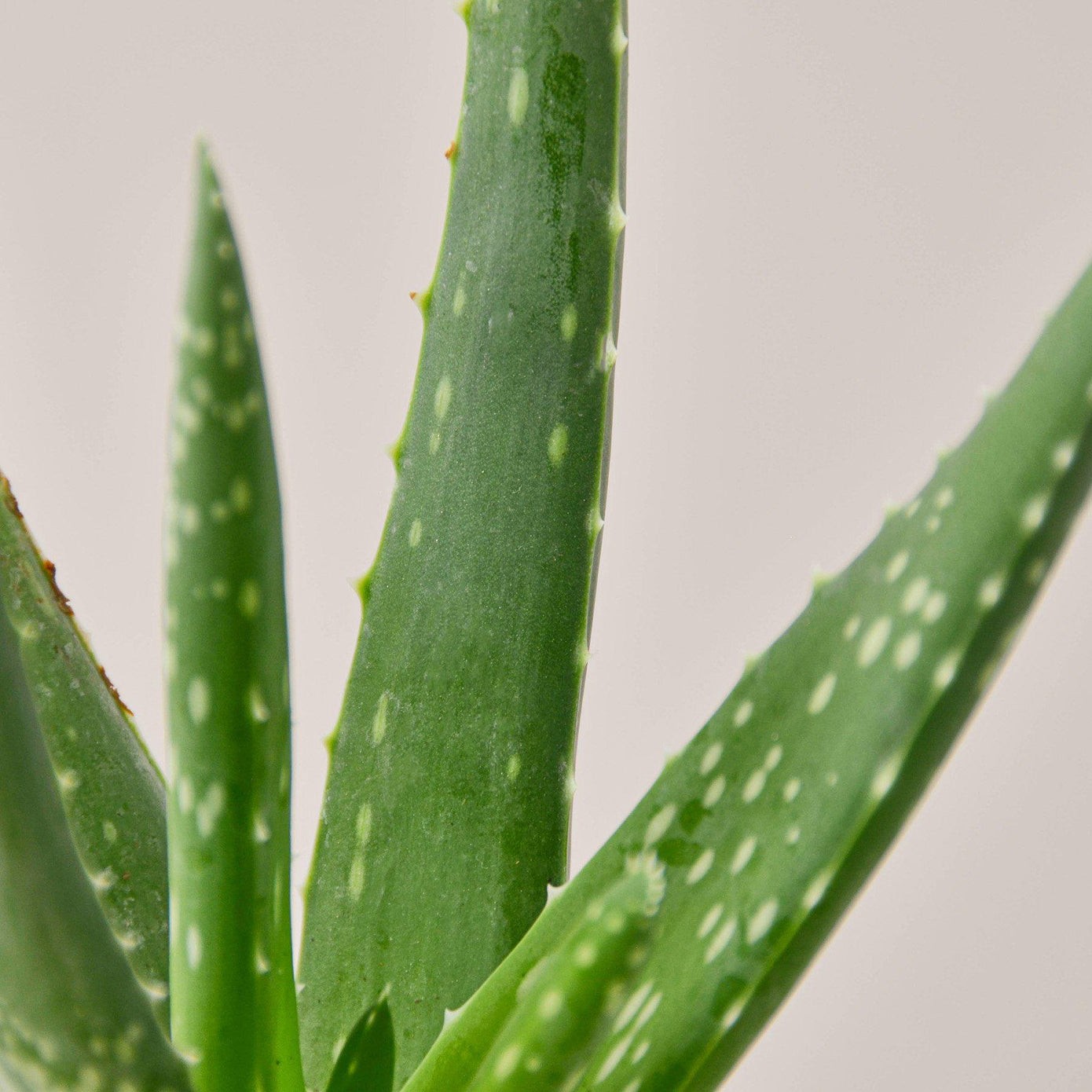
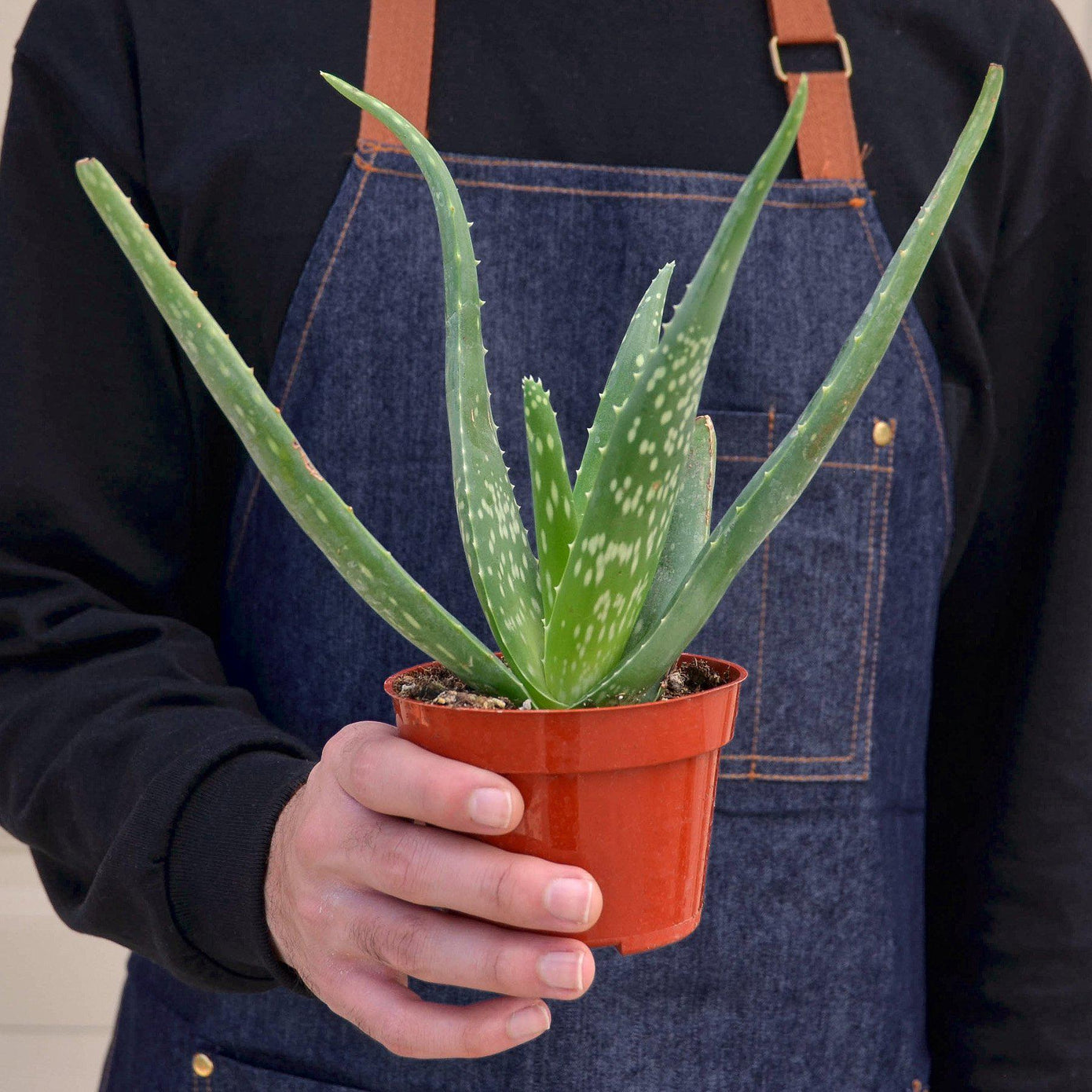
The Aloe Vera is a succulent plant renowned for its medicinal properties and striking appearance. Native to North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, this hardy plant is characterized by its fleshy, spiky leaves that are filled with a gel-like substance, commonly used in skin-care and health products. The thick, green leaves are often lined with small white teeth along the edges, and the plant produces a yellow tubular flower spike when in bloom, though it is more commonly cultivated for its leaves.
This low-maintenance plant thrives in warm, dry environments and is perfect for both beginner and experienced plant enthusiasts. Aloe Vera requires plenty of bright, indirect sunlight but can tolerate some direct sun, especially in the cooler months. It prefers well-draining soil and should be watered sparingly. Like many succulents, it is prone to root rot if overwatered, so the soil should be allowed to dry out completely between waterings. A pot with good drainage is essential to avoid stagnant water.
Aside from its beauty, this plant is best known for its soothing gel, which has been used for centuries to treat burns, cuts, and skin irritations. The gel inside the leaves has natural antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and cooling properties, making it a popular remedy for minor skin ailments. However, the sap of the plant, which can be found beneath the skin of the leaves, can be toxic if ingested, so caution is advised around pets and small children.
Note: While Aloe Vera is non-toxic to humans in moderation, it can cause gastrointestinal upset if consumed in large quantities, and it is toxic to pets, particularly cats and dogs, if ingested.
Care Insights & Expert Tips
- Don't overwater: The thick, fleshy leaves of Aloe Vera plants store water, so they may wrinkle slightly during dry conditions. If the leaves become brown or mushy, it may be a sign of overwatering or rot.
- Fertilize twice a year: Feed your Aloe Vera with a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength once or twice a year during the growing season.
- Propagates easily: Aloe Vera is easy to propagate from leaf cuttings or offsets.
- Repot with growth: Aloe Vera does not need frequent repotting. Repot the plant every 2-3 years or when it becomes too large for its container.

Visit our plant care library
Find essential tips to keep your plants thriving, vibrant, and healthy.